Arbitration
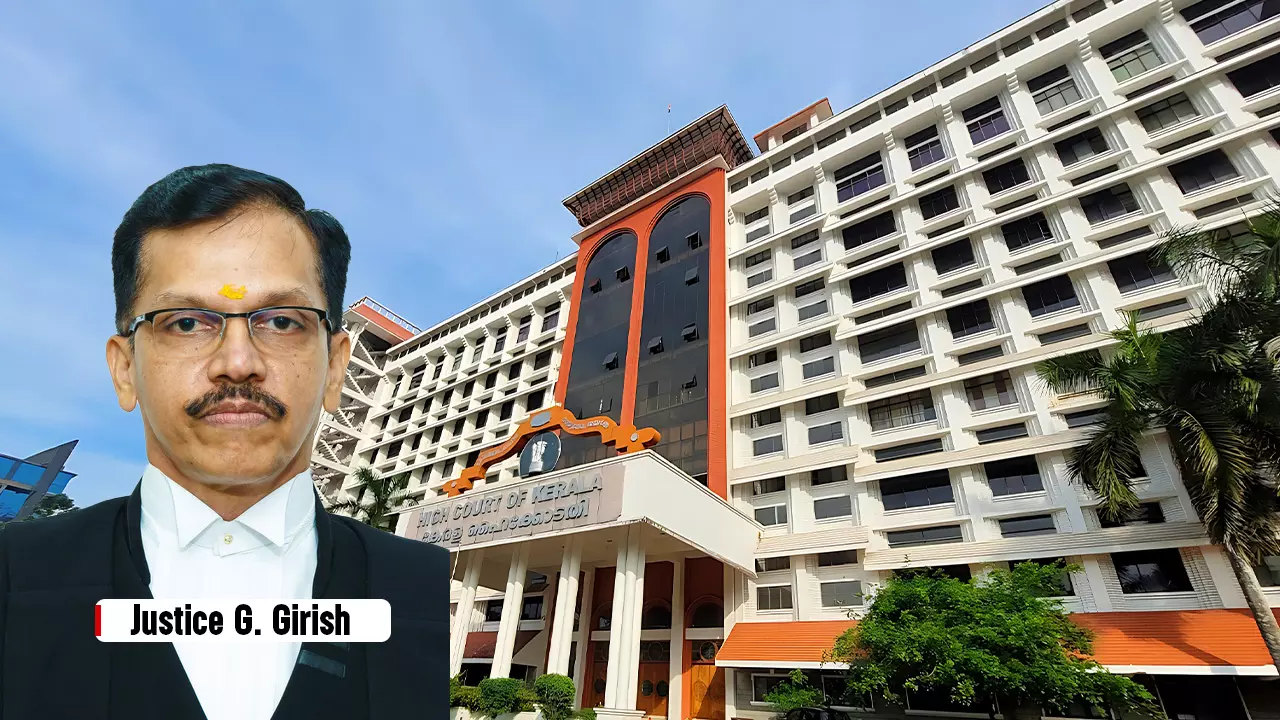
Appointment Of Arbitrator In Violation Of S. 12(5) Of A&C Act Is Void, Waiver Of This Provision Requires Explicit Written Agreement: Kerala High Court
The Kerala High Court single bench of Justice G. Girish held that the exemption provided for under the proviso of Section 12(5) of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act applies only in cases where there is a waiver explicitly agreed upon in writing by the parties involved. Section 12(5) provides that any person having a relationship with the parties, counsel, or subject matter of...
Court Has To Necessarily Extend Mandate Of The Arbitrator If No Ground For Its Substitution Is Made Out, No Need For A Separate Section 29A Application: Delhi High Court
The High Court of Delhi has held that a Court exercising powers under Sections 14 & 15 of the A&C Act can extend the mandate of the arbitrator if no ground for its substitution is made out in the application. The bench of Justice Neena Bansal Krishna held that once the Court is satisfied that there is no ground for substitution of the arbitrator, the Court can extend...
S. 9 Petition for Interim Relief in International Commercial Arbitration Not Classified as 'Arbitration Case', Must Be Filed as 'Miscellaneous Civil Case': Madhya Pradesh High Court
The Madhya Pradesh High Court division bench of Justice Sushrut Arvind Dharmadhikari and Justice Devnarayan Mishra dismissed a petition seeking interim relief under Section 9 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, stating it should have been filed as a 'Miscellaneous Civil Case' rather than an 'Arbitration Case' based on Chapter 2 of the Arbitration and Conciliation (Conduct of...
Arbitrator's Mandate Would Not Be Terminated When The Delays In Arbitral Proceedings Are Not Attributable To It: Bombay High Court
The High Court of Bombay has held that an arbitrator's mandate would not terminate when the proceedings are not completed within timelines agreed by the parties, if the delays in the conduct of the proceedings are attributable to the party seeking termination of the mandate. The bench of Justice Bharati Dangre held that generally, in an arbitration not governed by Section 29A,...
Arbitrator Failed To Deal With Material Contentions, Arbitral Award Would Not Satisfy The Requirement Of A Reasoned Award: Delhi High Court
The High Court of Delhi has held that when the arbitral tribunal fails to deal with submissions of a party on a contentious issue, the resultant award would not fulfil the requirements of a reasoned award as required under Section 31 of the A&C Act. It held that the tribunal cannot simply accept unquantified claims without assigning reasons and without dealing with the objections...
Arbitration Under Madhya Pradesh Madhyastham Adhikaran Adhiniyam, 1983 Cannot Be Invoked Without Availing Pre-Arbitral Remedy Within Limitation: Madhya Pradesh High Court
The High Court of Madhya Pradesh, at Jabalpur, has held that the Arbitration under Section 7 of the Madhya Pradesh Madhyastham Adhikaran Adhiniyam, 1983 cannot be invoked without first invoking the pre-arbitral in-house remedy provided under the agreement within the period of 30 days given under the Agreement. The bench of Justices Sheel Nagu and Vinay Saraf held that the...
Person Interested In Outcome Of Dispute Can't Appoint Arbitrator: Kerala High Court Nullifies Appointment Made By Kerala Government For Its Wholly Owned Undertaking
The Kerala High Court single bench of Justice G. Girish held that the appointment of a sole arbitrator by the Government of Kerala violated Section 12(5) of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996, as well as the precedent set by the Supreme Court in the Perkins Eastman case. The court held that the Government of Kerala being the holder of 99.99% of the equity shares...
If Arbitration Award Not Challenged Under Section 34, Can't Be Challenged At Execution: Madras High Court
The High Court of Madras at Madurai has held that an Executing Court cannot go behind an arbitration award and decides issues on merit of the award. The bench of Justice G. Ilangovan held that an arbitration award can only be challenged under Section 34 of the A&C Act and party failing to challenge the award therein cannot raise contentious issues on merit of the award before...
Mandate Of The Arbitrator Cannot Be Terminated When The Delay Was Not Attributable To Arbitrator: Delhi High Court
The bench of Justice Neena Bansal Krishna of Delhi High Court has held that mandate of the arbitrator cannot be terminated when the delay in proceedings was on account of pendency of appeal against the decision of the arbitral tribunal. The Court held that time consumed in the appeal and the consequent SLP and clarificatory applications cannot be attributed to the arbitral tribunal...
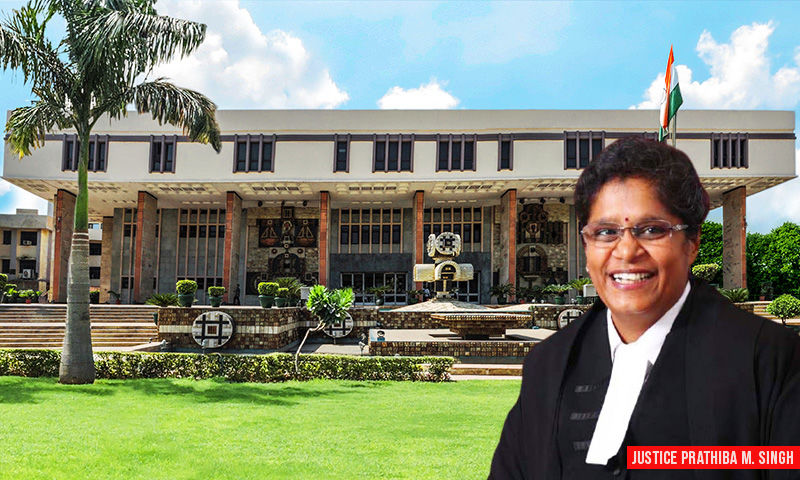
Arbitrator Appointment Cannot Be Called Unilateral When Respondent Consented To Appointment From Panel Of 5 Names: Delhi High Court
The High Court of Delhi has held that the appointment of the arbitrator cannot be called unilateral when the tribunal was constituted pursuant to the consent by the respondent to the appointment from a panel of 5 names. The Bench of Justice Prathiba M.Singh held that appointment of arbitrator from a panel of 5 names consisting of retired govt. officials would be valid in terms of...
Power Of General Manager Of Employer To Confirm Nomination Of Arbitrator By The Contractor Runs Contrary To Principles Of Impartiality And Independence: Bombay High Court
The High Court of Bombay has held that the power of General Manager of the employer to confirm nomination of arbitrator by the Contractor runs contrary to principles of impartiality and independence. It held that nomination by a party of its arbitrator cannot be subject to approval by the other party. The bench of Justice Bharati Dangre held that for an appointment of arbitrator from...
While Court's Jurisdiction Is Limited At The Time Of Making A Reference, It Is Not Expected To Mechanically Refer Dispute To Arbitration: Delhi High Court
The Delhi High Court single bench of Justice Dinesh Kumar Sharma has held that while the court's jurisdiction is limited at the time of making a reference, it is not expected to mechanically refer the dispute to arbitration. The Court also held that once a party has chosen to file a civil suit to get the disputes resolved, it cannot be permitted to invoke arbitration when the suit...