Arbitration
Arbitrator Terminating The Arbitral Proceedings Under Section 25(A) Of The A&C Act, Challenge Maintainable Under Article 227 Of The Constitution Of India: Delhi High Court
The Delhi High Court has ruled that since no alternate remedy is available to the claimant to challenge the order of the arbitrator terminating the arbitral proceedings under Section 25(a) of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 (A&C Act), hence, a petition under Article 227 of the Constitution of India against the said order of the arbitrator is ex...
The Weak Financial Condition Of A Party Cannot Be The Sole Ground To Deposit Security Or Bank Guarantee: Delhi High Court
The High Court of Delhi has held that the weak financial condition of a party cannot be the sole ground to direct the party to deposit a security or bank guarantee to secure the amount involved in the arbitration. The Single Bench of Justice Anup Jairam Bhambhani has held merely because a party is in financial distress, it cannot be the sole ground to direct it to deposit the...
If The Contract Is Extended By The Employer, It Cannot Be Allowed To Reduce The Period Of The Extension Retrospectively: Delhi High Court
The High Court of Delhi has held that when the employer has granted the contractor an extension of time for a specified period, it cannot turn around to contend that the extension was only provisional and it is allowed to reassess or reduce the number of days by which the execution of the contract was executed. The Single Bench of Justice Sanjiv Sachdeva has held that once the...
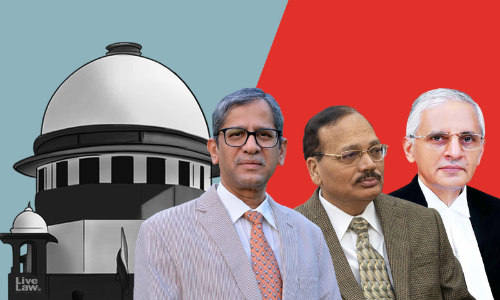
"Group Of Companies" Doctrine Needs Relook, Says Supreme Court; Refers Issues To Larger Bench
The Supreme Court, on Friday, referred various aspects regarding the application of the doctrine of 'Group of Companies', which is often utilised to bind non-signatories to an Arbitration Agreement, to a larger Bench."There is a clear need for having a relook at the doctrinal ingredients concerning the group of companies doctrine", observed a Bench comprising Chief Justice of India,...
Inordinate And Unexplained Delay In Rendering Arbitral Award Is Against Public Policy Of India: Delhi High Court
The Delhi High Court has ruled that inordinate and unexplained delay in rendering the arbitral award is in conflict with the public policy of India and is amenable to challenge under Section 34 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 (A&C Act). The Single Bench of Justice Vibhu Bakhru held that award of damages arbitrarily and without any basis also falls foul of the...
Power Of Arbitral Tribunal To Award Interest Is Discretionary & Subject To Agreement Between Parties: Supreme Court
The Supreme Court has held that the power of the arbitral tribunal to award interest is subject to an agreement between the parties to the contrary. The Court held that the tribunal cannot award interest if the parties have agreed otherwise. The Division Bench of Justice L. Nageshwar Rao and Justice B.R. Gavai held that when the parties have an agreement between themselves that...
Second Application For Appointment Of Arbitrator Is Maintainable, Even Though No Liberty Has Been Granted By Court While Setting Aside The Award: Jharkhand High Court
The Jharkhand High Court has ruled that after an arbitral award has been set aside and quashed by the Court under Section 37 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 (A&C Act), an application under Section 11(6)(c) of the A&C Act for appointment of an arbitrator afresh is maintainable, even though no liberty has been granted by the Court while passing the order...
Section 47 Of CPC Is Not Attracted In Proceedings For Execution Of An Arbitral Award: Telangana High Court
The Telangana High Court has ruled that in proceedings for execution of an arbitral award the whole gamut of CPC is not attracted, and a Court while dealing with an application under Section 36 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 (A&C Act) for enforcement of an award is not bound by the provisions of Section 47 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 (CPC) and is not required...
Application Under Section 11(6) Not Maintainable For Appointment Of Arbitrator In Absence Of A Written Agreement Between Parties: Supreme Court
The Supreme Court has ruled that there is a difference between the arbitrator appointed under Section 11(5) and under Section 11(6) of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 (A&C Act) and failing any written agreement between the parties on the procedure for appointing an arbitrator (s) under Section 11(2), application for appointment of arbitrator (s) shall be maintainable...
Post-Award Interest Is Not Advisory But A Mandate Of The A&C Act: Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court has ruled that award of future or post-award interest is not advisory but a mandate of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 (A&C Act) and it should be given its due weightage. The Single Bench of Justice Moushumi Bhattacharya reiterated that post award interest is a safeguard against delayed payment of the amount awarded to the award...
Weekly Round-Up of Arbitration Cases : April 24 to April 30, 2022
Supreme Court Group Of Companies Doctrine Can Be Applied To Bind Non Signatory To An Arbitration Agreement: Supreme Court Case Title: Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd. versus Discovery Enterprises Pvt. Ltd Citation: 2022 LiveLaw (SC) 416 The Supreme Court, in a judgment delivered on 27th April 2022, explained the 'Group of companies' doctrine which postulates...
Arbitral Award Not Providing Statutory Compensation On Land Acquired Under NHA Is Perverse: Madras High Court
The Madras High Court has held that an arbitral award that does not provide for payment of mandatory statutory compensation with respect to the land acquired under the National Highways Act, 1956 is perverse. The Single Bench of Justice P.T. Asha held that an Arbitrator exercising jurisdiction under the National Highways Act has to be more vigilant in ensuring that the arbitral award...